What is Reverse Logistics?
Logistics refers to the process by which goods move from manufacturers or distributors to consumers. But what about the process where goods already sold return to the manufacturer or distributor, such as returns or recalls? This is known as reverse logistics, the flow of goods in the opposite direction. Companies without a proper reverse logistics process often face problems in various aspects, including inventory management. Let's take a closer look at the types of reverse logistics and the efficient reverse logistics process!
What is Reverse Logistics?
Reverse logistics refers to the logistics process where goods delivered from suppliers (companies) to consumers are returned back to the suppliers.
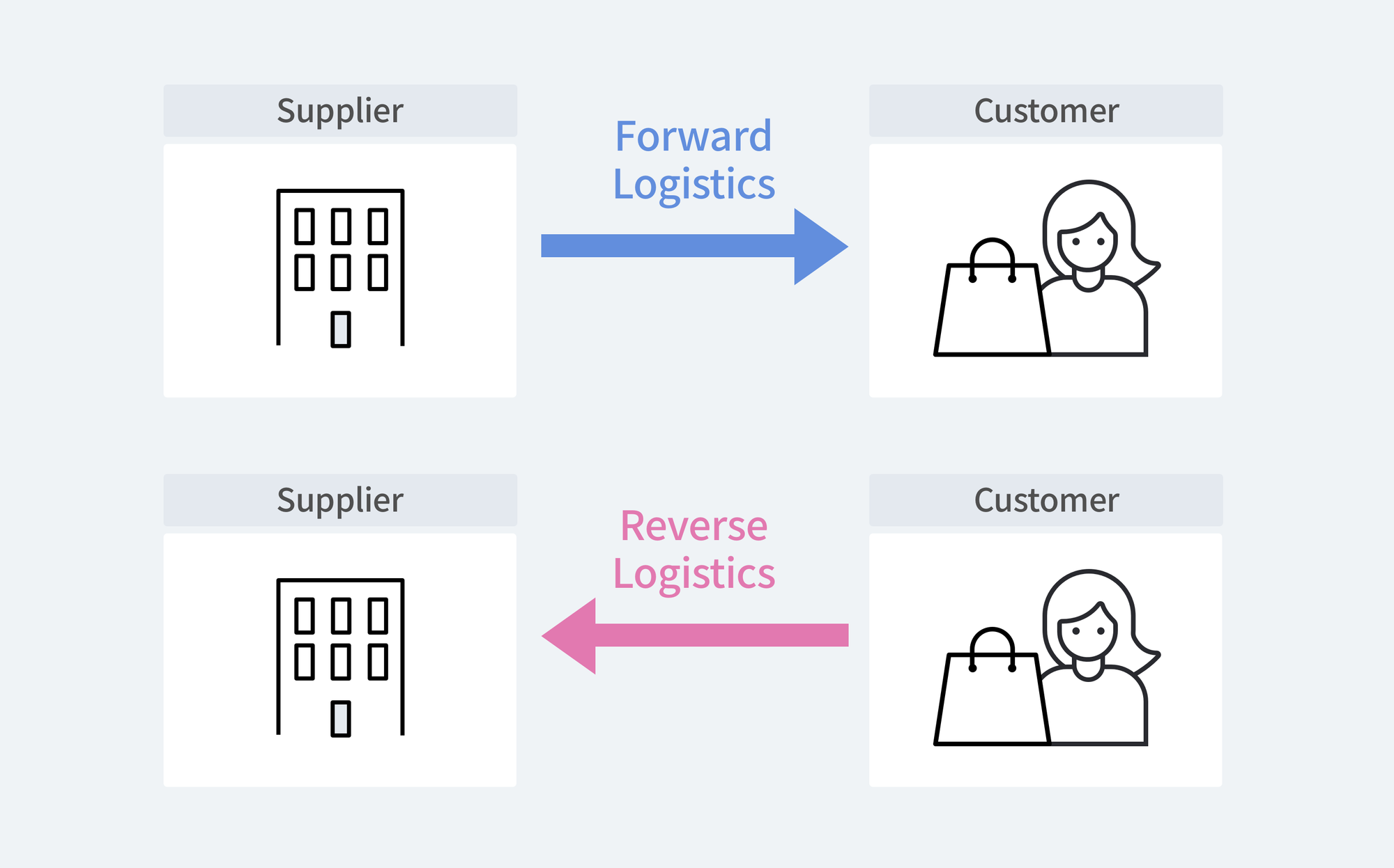
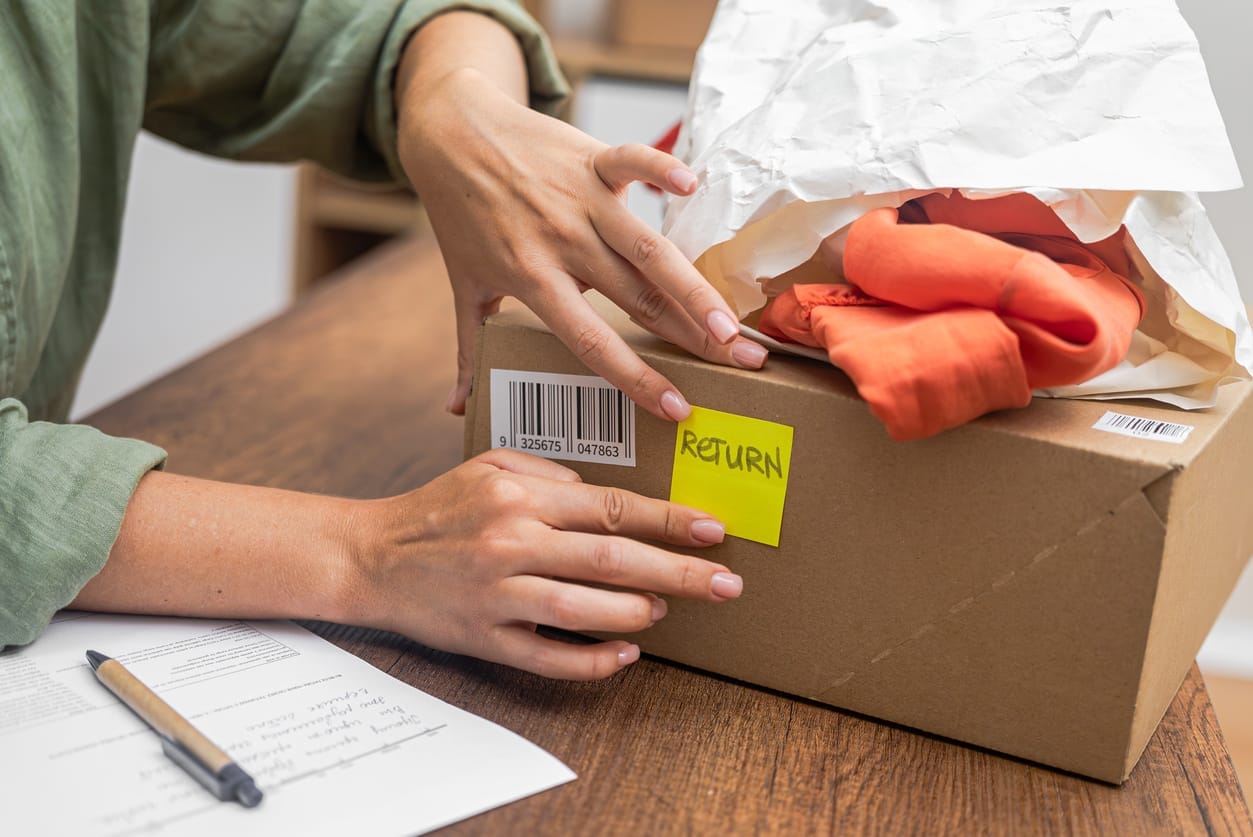
Even though the term "reverse logistics" may seem unfamiliar, we encounter various forms of reverse logistics in our daily lives. The most typical example of reverse logistics is returns. As the online shopping market, where goods are purchased without direct inspection, grows, companies face the significant challenge of handling returns. Items like clothes or shoes are often returned because they don't fit or suit the individual. Sometimes, goods are returned due to damage incurred during inspection or delivery. Goods returned to the supplier are processed differently depending on their condition. Products returned due to simple change of mind, without any defects, are restocked, while damaged products undergo repair, reprocessing, recycling, or disposal.
Recalls of defective goods are another example of reverse logistics, also known as return logistics, which includes policies by companies to dispose of products that have reached the end of their life cycle. Some companies offer a certain amount of credit for returning old products. For expensive items like electronic products, recycling parts from old products is much more economical. Some companies aim to minimize environmental impact through such returns. For example, Apple and Samsung have trade-in policies for returning old products, and capsule coffee companies like Nespresso have collection policies that involve taking back used capsules in recycling bags.
Efficient Reverse Logistics Process
Not all consumers request returns or collections, making reverse logistics unpredictable. Therefore, many companies neglect to build a reverse logistics process. However, reverse logistics is indeed a part of the value chain that delivers the company's value to customers. If you want to build a positive brand image, it's important to be well-informed about efficient reverse logistics processes. Let's look at the step-by-step process of well-established reverse logistics, focusing on returns!

1. Customer Request Reception
The reverse logistics process always starts with a customer's request. Companies need to systematize the return request process so it's not cumbersome for customers. Once a customer request is received, the product must be collected quickly and agilely. To minimize customer inconvenience during this process, many companies have introduced automation systems.
2. Category Classification
The core of the reverse logistics process is classification. Depending on the reason for the return, the same product can have a big difference in quality. For example, a product returned without being opened by the customer can be resold without any reprocessing. However, reselling a damaged product without repair or reprocessing could worsen the brand image. In such cases, options for repair, reprocessing, recycling, or disposal need to be considered.
3. Inventory Management
Once reverse logistics products are classified by category, they must be stored safely in the appropriate place. The most important point here is to manage the new products, reverse logistics products, and products by category separately to avoid critical mistakes, such as mistaking returned inventory for new product inventory.
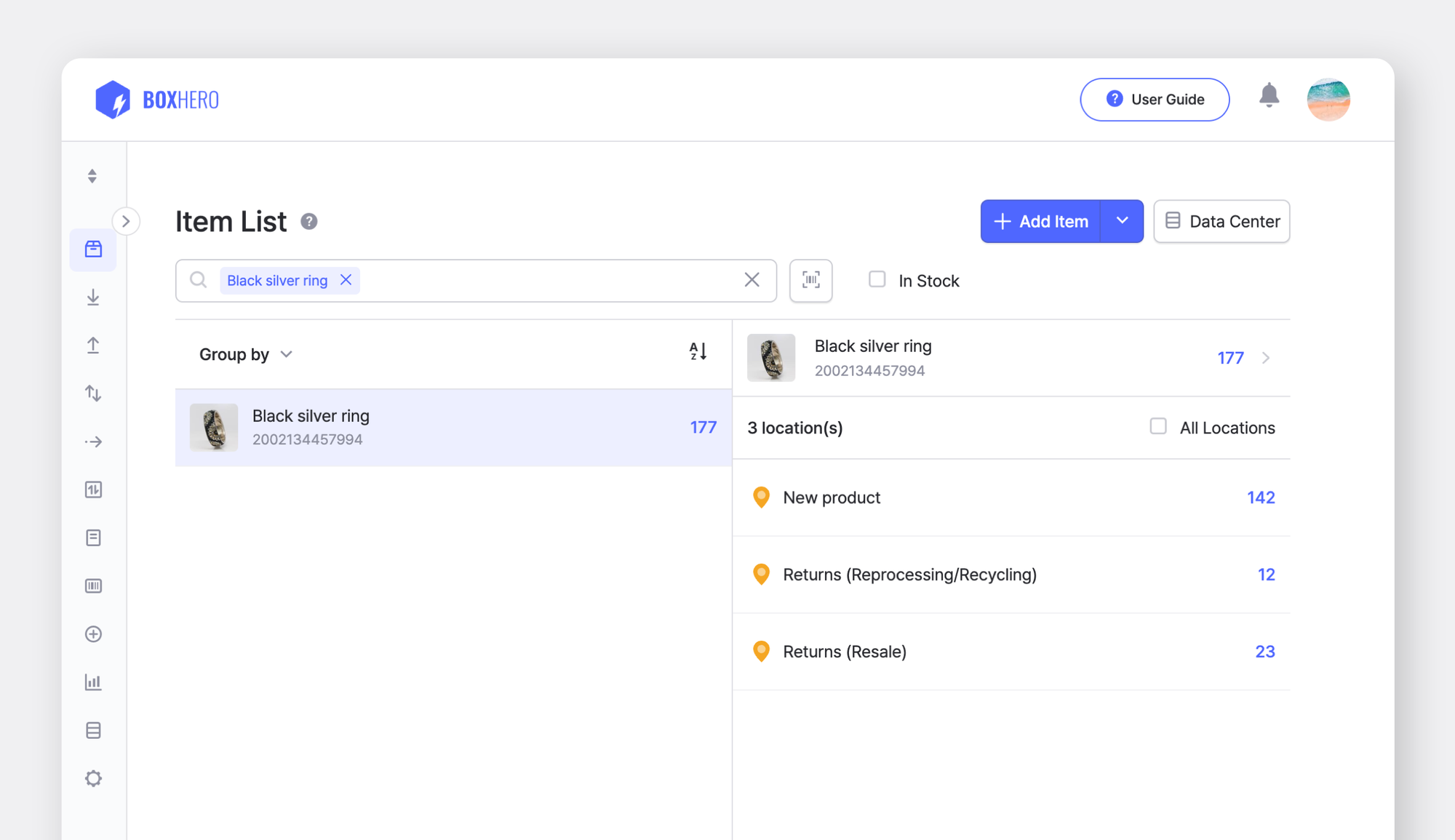
4. Disposal
Finally, appropriate measures are taken according to the category. Healthy products go through repackaging and restocking, while products with functional integrity but cosmetic damage can be sold as refurbished items at a discount. Products that have reached the end of their life cycle are reprocessed/recycled for parts, and other products are disposed of in a way that minimizes environmental impact.
There's no need to view returned products negatively. Efficient reverse logistics can actually serve as an opportunity to strengthen a brand image. If you're facing difficulties with inventory management during the reverse logistics process, consider using an inventory management solution like BoxHero! It makes managing reverse logistics products easy and convenient.


